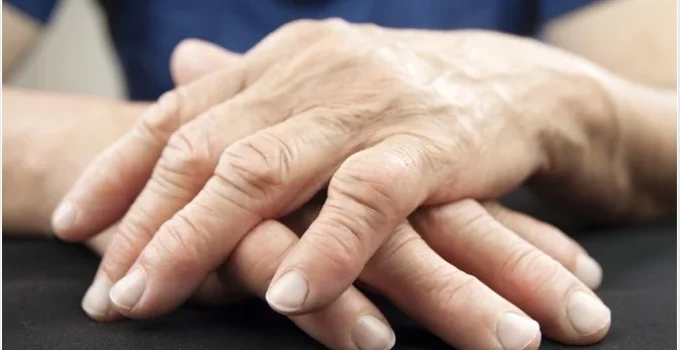
Arthritis is a common medical condition characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation, affecting millions of people worldwide. With over 100 different types of arthritis, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments is essential to manage this chronic disease effectively. This article will explore the different types of arthritis, self-care measures, and medical intervention options to help you better understand this debilitating condition.
Different Types of Arthritis
Source: medlineplus.gov
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, affecting millions of individuals. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints wears away, causing bones to rub against one another. This friction leads to pain, stiffness, and inflammation. OA commonly affects the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
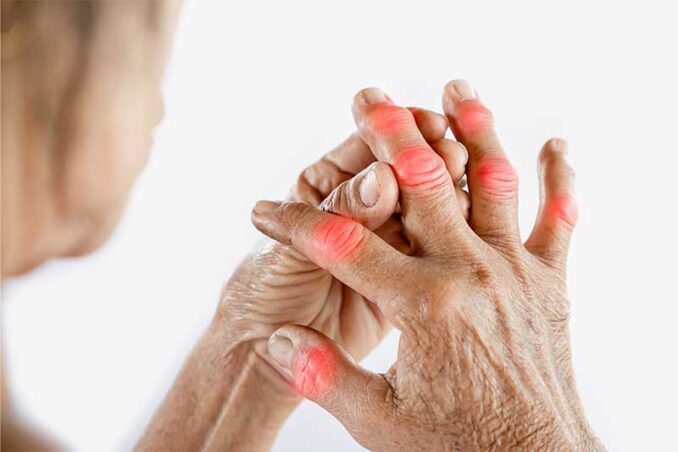
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and pain. Over time, this inflammation can damage the joints, leading to deformities and disability. RA typically affects the hands, wrists, and feet.
3. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Psoriatic arthritis is a form of arthritis that affects individuals with the skin condition psoriasis. PsA can cause joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, as well as skin symptoms like redness, scaling, and itching. It typically affects the joints of the fingers, toes, and spine.
4. Gout
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid in the blood. This excess uric acid can form crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling. Gout commonly affects the big toe but can also involve other joints.
5. Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine. It causes inflammation in the vertebrae, leading to pain and stiffness in the back, neck, and hips. Over time, AS can cause the vertebrae to fuse, limiting mobility and flexibility.
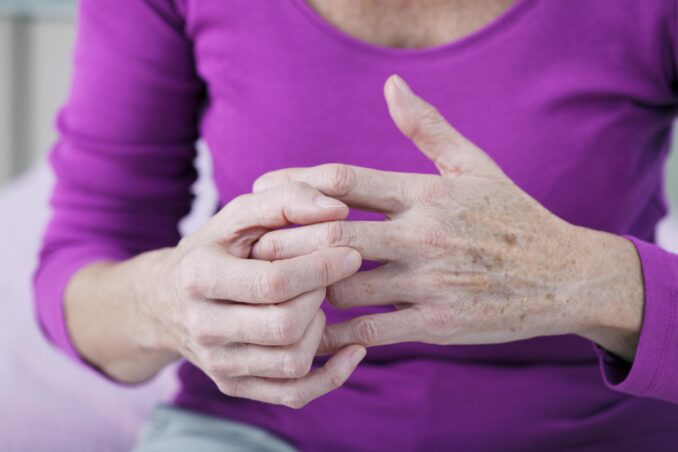
Self Care for Arthritis

Source: friendlyshoes.com
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can put additional stress on weight-bearing joints, worsening arthritis symptoms. Losing weight can help alleviate pain, improve joint function, and slow the progression of the disease.
2. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise can help maintain flexibility, reduce joint stiffness, and build muscle strength to support the joints. Low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and cycling are suitable for individuals with arthritis.
3. Apply Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat therapy, such as warm baths or heating pads, can help relax muscles and alleviate joint stiffness. Cold therapy, like ice packs, can help numb pain and reduce inflammation. Experiment with both to find the most effective relief for your symptoms.
4. Use Assistive Devices
Assistive devices like canes, walkers, and splints can help provide additional support and alleviate joint stress. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable devices for your needs.
5. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Stress can exacerbate arthritis symptoms, so incorporating relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
Medical Intervention for Arthritis
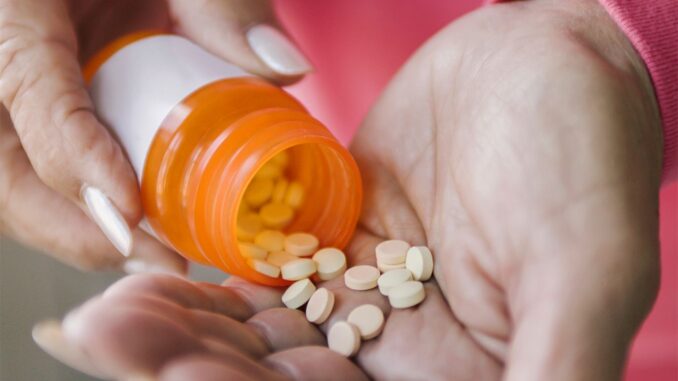
Source: everydayhealth.com
Medications
Various medications can help manage arthritis symptoms and slow disease progression. These include:
Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate mild to moderate arthritis pain.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications reduce inflammation and pain, and are available in both over-the-counter and prescription strengths. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib.
Corticosteroids: These powerful anti-inflammatory drugs can be taken orally or injected directly into the affected joint to provide rapid relief of symptoms.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These medications are used primarily for RA and PsA, as they work to slow disease progression and prevent joint damage. Examples include methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and leflunomide.
Biologic agents: These are a newer class of DMARDs that target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation. They are often used in combination with conventional DMARDs for RA and PsA. Examples include etanercept, adalimumab, and infliximab.
- Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help improve joint function, mobility, and strength. A physical therapist can develop a personalized exercise program to address your specific needs, as well as teach you proper body mechanics to protect your joints.
- Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists can help individuals with arthritis learn new ways to perform daily tasks and activities to reduce joint stress and improve overall function. They can also recommend assistive devices and adaptive equipment to help make tasks easier and less painful.
- Joint Injections
Joint injections can help provide short-term pain relief and reduce inflammation. These injections may include corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid, a substance that mimics the lubricating properties of joint fluid.
- Surgery
In severe cases where conservative treatments are not effective, surgery may be recommended from a specialized orthopedic surgeon like Integrated Orthopedics. Surgical options depend on the type of arthritis and the affected joint, but may include:
- Joint replacement: Damaged joints can be replaced with artificial components, restoring function and relieving pain. Common joint replacements include hip, knee, and shoulder.
- Joint fusion: In this procedure, the bones in a joint are fused together, providing stability and pain relief. This is often done for smaller joints like those in the wrist, ankle, or fingers.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves using a small camera to visualize and treat joint problems, such as removing damaged cartilage or repairing torn ligaments.

Source: nextcare.com
Arthritis is a complex and diverse group of conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the different types of arthritis, incorporating self-care measures, and seeking appropriate medical intervention can help manage symptoms and maintain joint health. If you suspect you may have arthritis, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific needs.