Although most of us use smartphones, tablets, computers, and laptops on a daily basis, only a few stops to consider the ramifications of manufacturing all of these devices. More importantly, we need to stop and consider where old discarded mobile phones and other devices would go and what discarding all of these devices will cost our planet and, subsequently, our future.
While smartphones and electronic gadgets are not solely responsible for the E-waste crisis of our world since larger home appliances participate in the increasing numbers of E-waste, smaller personal devices are the focus of E-waste as they are larger in numbers and faster to be deprecated and updated than household appliances such as a fridge for example.
So, as electronic devices become more and more of a life necessity for every person on the planet, the problem of E-waste continues to grow by the ton every day. Most devices get obsolete within a couple of years and many are thrown away before they are even obsolete.
Thankfully, E-waste management comes into the picture to save the day and control the ever-growing mountains of electronic waste that humans keep producing every day.
In this post, we’re going to take a deep look at the E-waste management market, the positive effect it has on the planet, and the rules that every organization should take into consideration when it comes to E-waste management in general.
The E-waste problem in numbers
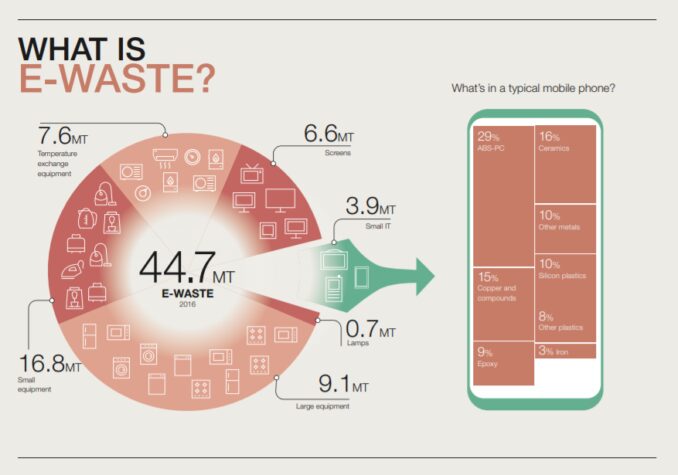
Source:weforum.org
Each year, there are at least a dozen new smartphone releases from major companies around the world. As users try their best to keep their smartphone devices up-to-date, thousands, if not millions, of devices are turned into E-waste in order for the new models to take their places.
Since plastic is one of the main players in the smartphone manufacturing game, dealing with Smartphones E-waste is almost impossible. According to a 2017 survey, almost 40% of smartphone users replace their devices within a year, every year.
The overall E-waste production is estimated between 40 and 50 million tons every year worldwide. If you want to imagine what this amount would look like, visualize a window open to the street, and every single second, there are 800 laptops thrown out of that window. Hard to imagine, right?
Moreover, electronic waste represents about 70% of the entire planet’s toxic waste. Given that this waste is hard, if not impossible, to get rid of since it is mostly plastic, most of the waste of electronics ends up in landfills where the only solution left to get rid of it is to burn it!
Only about 15% of E-waste is recycled which leaves the Earth with 85% of this toxic waste to be turned into toxic air later on.
The problem with E-waste does not stop at the plastic issue. When it comes to smartphones, for example, a considerable amount of rare and precious metals such as gold, silver, and copper are used in the manufacturing process. So, when mobile phones are thrown away and become E-waste a percentage of the world’s gold is lost forever with that phone. The US yearly E-waste contains about $60 million in both gold and silver.

Source:indiamart.com
E-waste management as a solution
With the word “Management” the mind immediately goes to organizations in the sense that there must be some committee responsible for it. While this is true with the case of the National Environment Agency (NEA) in Singapore, for example, the term “E-waste management” should not be exclusive to these entities.
Since smartphones, one of the largest contributors to the E-waste crisis, are personal devices, E-waste management should be a personal responsibility of every individual who uses electronic devices as well as the companies that operate in the electronics industry.
What is E-waste management?
While the name may indicate a complicated process, E-waste management is essentially about how we handle the old devices such as laptops and mobile phones for example.
So, all the process of E-waste management entails is to repair, reuse, donate, and recycle old electronics.
As you can see by now, these are all activities that can be done on a personal level as well as organization and corporation levels.
While companies can achieve the same result on a larger scale due to their larger level of electronic consumption per year, individuals as well can do their part by choosing to sell their old devices to a refurbishing service such as refurbishment centres which will make the most out of these devices instead of having them laying around at home by their old owners.
You see, by choosing to donate or sell your old smartphone, you will be reducing the E-waste amount as well as making a profit compared to throwing the phone away or in your drawer.
E-waste management rules in India

Source:pinterest
While E-waste management is certainly the best option compared to having millions of tons of old and broken electronics in landfills, there are still certain rules that should be followed in any E-waste management process.
In 2011, the Indian Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change set the rules for E-waste management. These rules were upgraded with several amendments most famously in 2016 and 2018.
In order not to take you into deeper and confusing details, this section is going to be about the general Dos & Don’ts of the E-waste management recommendations.
Dos of E-waste management

Source:news.itu.int
Most electronic devices should come with instructions as to how to handle the product at the end of its life.
Make sure that you’re allowing an authorized recycling organization to recycle your devices.
Deliver your old smartphones, laptops, tablets, and batteries to the nearest E-waste collection locations as assigned by your local authorities.
Before sending any device for recycling, make sure that you remove and separate the battery and that there are not shards of broken glass.
Don’ts of E-waste management
Don’t throw old electronics in regular trash bins.
Don’t break or tear old electronic devices before disposing of them.
Don’t give your old devices to an unknown source for recycling.
Don’t leave old data of yours on a device when it’s time for it to be recycled.
The E-waste management market in numbers
There is much more benefit to the E-waste management market than saving the environment as it can save the economy as well. The phrase “one man’s trash is another man’s treasure” comes to mind when inspecting the numbers of the E-waste management market growth.
In 2019, the E-waste management market size was estimated by $41.97 billion. By 2027, this number is expected to reach $102.62 billion with a growth rate of 11.9%.
The most famous business operating in E-waste management marketing are refurbishing business that takes old devices that need a little work to be returned to its pristine condition and then re-sell theses devices for a lower price than its brand-new prices.
Even devices that are beyond economic repair are being utilized by refurbishing centres such as QwikFone where BER devices are used as spare parts for devices that might need a part or two replaced to be as good as new again. Using original parts from BER devices to renew refurbished electronics is the best usage for these items that would, otherwise end up in landfills. This way, the cost is lowered and, therefore, the prices are lowered as well.
However, electronics manufacturers have a great role in the E-waste management issue as well. Building devices that would last longer than a year would definitely have a great effect on lowering the millions of tons of E-waste produced every year.
Conclusion

Source:global-recycling.info
Small electronics and personal devices such as tablets and phones are accounted for the largest portion of the global E-waste crisis. The reason for this is that while a an entire household can purchase a single refrigerator and keep using it for years, every single person living in this house would require their own smartphone / tablet and then buy a new one for every one within the span of one year. This translates into mass production that is far greater than large electronics.
Moreover, it seems that smartphone manufacturers, for example, are building their devices to last as little as possible to increase the consumers’ needs to upgrade as soon as possible.
All of these issues directly contribute to the E-waste issue the world is facing.
With the E-waste management market, not only is there a way to lighten the world’s load of toxic waste that would last for hundreds of years without degrading, but an income and profit generating aspect of the market is helping the economy of different countries to come out of its rut.
With too many businessmen and influential people wrongfully stating that caring for the environment and our planet is bad for the economy, it is certainly a breath of fresh air to find others who invest and start businesses in a market that actually has the goal of saving the environment in mind in addition to turning profit and growing the capital in addition to profits.





