The Current Landscape of Glioblastoma Treatment
The current treatment options for glioblastoma typically include a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. While these approaches have shown some success in prolonging survival and managing symptoms, there are several challenges and limitations associated with current glioblastoma treatment.
1. Understanding Glioblastoma: An Aggressive Brain Cancer
Glioblastoma is an aggressive form of brain cancer that affects thousands of individuals each year. It is characterized by its ability to spread rapidly within the brain, making it extremely difficult to treat effectively.
Glioblastoma, also known as glioblastoma multiforme, is the most common and aggressive type of brain tumor. It originates in the glial cells, which are supportive cells in the brain. Glioblastoma tumors are characterized by their infiltrative nature, meaning they invade and spread rapidly within the brain tissue. This invasive behavior makes complete surgical removal of the tumor nearly impossible, as some tumor cells are left behind even after surgery.
Furthermore, glioblastoma is a heterogeneous cancer, meaning it consists of different cell types with varying genetic characteristics. This heterogeneity makes treatment challenging, as the tumor cells may respond differently to different therapies. Additionally, glioblastoma tumors have a high propensity for recurrence, with new tumors often appearing in other areas of the brain even after successful treatment.
2. Traditional Treatment Approaches: Surgery, Radiation, and Chemotherapy
The standard treatment protocol for glioblastoma typically involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Surgery is performed to remove as much of the tumor as possible while minimizing damage to healthy brain tissue. However, due to the infiltrative nature of glioblastoma, complete surgical removal is often not achievable.
After surgery, radiation therapy is administered to target any remaining tumor cells and help prevent recurrence. This involves the use of high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy, often in the form of oral or intravenous medications, is used to target any remaining tumor cells and slow down the growth of new cells. However, chemotherapy is limited by its inability to specifically target glioblastoma cells, leading to potential damage to healthy cells.
3. Challenges and Limitations in Current Glioblastoma Treatment
Despite the current treatment approaches, glioblastoma remains a highly aggressive and challenging cancer to treat. One of the major challenges is the blood-brain barrier, a protective mechanism that prevents many drugs from effectively reaching the brain. This limits the effectiveness of chemotherapy and other systemic therapies in treating glioblastoma.
Another limitation is the development of resistance to treatment over time. Glioblastoma cells can adapt and become resistant to the effects of radiation and chemotherapy, leading to recurrence and disease progression. Additionally, the invasive nature of glioblastoma makes it difficult to completely remove all tumor cells, contributing to the high rate of recurrence.
Furthermore, the heterogeneity of glioblastoma tumors poses challenges in identifying effective treatment strategies. Different tumor cells may respond differently to treatment, making it difficult to develop therapies that can effectively target all cell types within the tumor.
Revolutionary Innovations in Glioblastoma Treatment

Source: michiganmedicine.org
Despite the challenges and limitations, there have been significant advancements in glioblastoma treatment, offering hope for patients. These innovative approaches aim to overcome the barriers in current treatment options and provide more targeted and effective therapies.
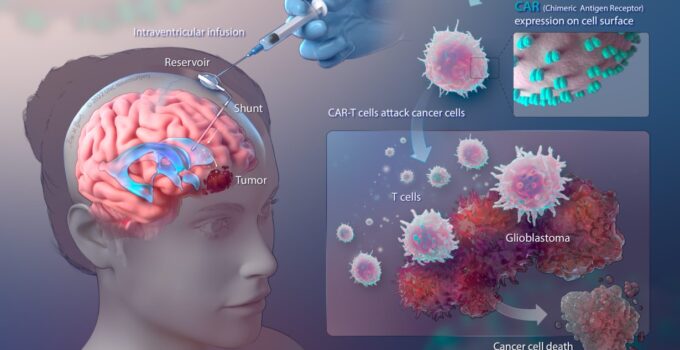
1. Immunotherapy: Harnessing the Power of the Immune System
Immunotherapy is a cutting-edge treatment approach that utilizes the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells. It works by stimulating the immune system or engineering immune cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells. In the case of glioblastoma, immunotherapy holds great promise in improving treatment outcomes.
One type of immunotherapy being explored for glioblastoma is immune checkpoint inhibitors. These drugs target specific proteins on immune cells or cancer cells, allowing the immune system to better recognize and attack the tumor. Another approach is the use of cancer vaccines, which are designed to stimulate the immune system to recognize and target glioblastoma cells.
2. Targeted Therapies: Personalized Medicine for Glioblastoma
Targeted therapies are designed to specifically target the genetic alterations or molecular characteristics of cancer cells. They offer the potential for more precise treatment and reduced side effects compared to traditional therapies. In glioblastoma, targeted therapies are being developed to attack specific molecular pathways that are critical for tumor growth.
One example of a targeted therapy for glioblastoma is the use of inhibitors that target the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). EGFR is a protein that plays a key role in cell growth and division, and its mutation is commonly found in glioblastoma. By blocking the activity of this protein, targeted therapies can inhibit tumor growth and potentially improve patient outcomes.
3. Novel Approaches: Gene Therapy and Nanotechnology

Source: ophthalmologytimes.com
Gene therapy and nanotechnology are emerging fields that hold promise in glioblastoma treatment. Gene therapy involves introducing genetic material into cells to correct or modify their function. In the case of glioblastoma, gene therapy can be used to deliver therapeutic genes directly to the tumor cells, inhibiting their growth or promoting their destruction.
Nanotechnology, on the other hand, involves the use of nanoparticles to deliver drugs or therapeutic agents directly to the tumor site. These nanoparticles can be designed to specifically target glioblastoma cells, bypassing the blood-brain barrier and delivering treatment directly to the tumor while minimizing damage to healthy cells.
Promising Clinical Trials and Breakthrough Research
Clinical trials play a crucial role in advancing glioblastoma treatment by evaluating the safety and efficacy of novel therapies. Several clinical trials are currently underway, exploring new treatment strategies and combination therapies for glioblastoma.
1. Advanced Clinical Trials: The Hope for Glioblastoma Patients
Advanced clinical trials often involve experimental treatments that have shown promising results in preclinical studies. These trials evaluate the safety and efficacy of these new approaches in a controlled setting with a small group of patients. Some ongoing clinical trials in glioblastoma include testing novel immunotherapies, targeted therapies, and combination treatments.
One particular area of interest is the use of combination therapies, where multiple treatment approaches are used together to enhance efficacy. For example, combining immunotherapy with targeted therapies or chemotherapy may help overcome resistance mechanisms and improve treatment outcomes.
2. Emerging Treatment Strategies: Combining Therapies for Enhanced Efficacy
Emerging treatment strategies in glioblastoma aim to combine multiple treatment modalities to improve outcomes. One approach is the use of localized therapies, such as tumor-treating fields (TTFs), in combination with standard treatments. TTFs are low-intensity electric fields that disrupt the division of cancer cells and have shown promising results in extending survival in glioblastoma patients.
Another emerging strategy is the use of immunotherapy in combination with other therapies, such as radiation or targeted therapy. By targeting the immune system and the tumor cells through different mechanisms, combination therapies have the potential to improve treatment response and overcome resistance.
3. Promising Research and Potential Future Breakthroughs
Continued research into glioblastoma has identified several potential future breakthroughs that may revolutionize treatment options. One area of focus is the development of new drug delivery systems that can overcome the blood-brain barrier and deliver targeted therapies directly to the tumor site.
Additionally, advancements in genomics and molecular profiling have enabled researchers to better understand the genetic characteristics of glioblastoma. This knowledge can inform the development of more personalized treatment strategies that target the specific genetic alterations present in individual patients.
Furthermore, research into the tumor microenvironment and the interactions between tumor cells and surrounding cells is shedding light on potential therapeutic targets. By targeting these interactions and disrupting the supportive environment for tumor growth, researchers hope to develop more effective treatments for glioblastoma.
Improving Quality of Life for Glioblastoma Patients
Source: clinicalconnection.hopkinsmedicine.org
While the focus of glioblastoma treatment is on extending survival and improving outcomes, it is equally important to prioritize the quality of life for patients. Glioblastoma can have numerous physical, emotional, and psychological effects on patients, and supportive care plays an important role in addressing these challenges.
1. Palliative Care: Enhancing Comfort and Well-being
Palliative care focuses on managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients with serious illnesses, such as glioblastoma. It involves a multidisciplinary approach, addressing the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients and their families.
Palliative care teams work closely with patients to provide pain management, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall well-being. This holistic approach ensures that patients receive the necessary support to enhance their comfort and maintain a sense of dignity and quality of life.
2. Integrative Therapies: Complementary Approaches for Supportive Care
Integrative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, and yoga, can play a valuable role in supporting the well-being of glioblastoma patients. These therapies focus on integrating physical, mental, and emotional aspects of health and can help alleviate symptoms, reduce stress, and promote relaxation.
Additionally, complementary approaches like nutritional counseling and mind-body techniques, such as meditation and mindfulness, can provide patients with tools to cope with the challenges of living with glioblastoma and improve their overall quality of life.
3. Psychological Support: Nurturing Mental Health and Emotional Well-being
Glioblastoma can have a significant impact on the mental health and emotional well-being of patients, as well as their families. It is important to provide psychological support and counseling services to help patients navigate the emotional challenges associated with their diagnosis and treatment.
Psychologists and counselors can help patients and their families cope with feelings of anxiety, depression, and grief, providing a safe space to express their emotions and develop effective coping strategies. Support groups and peer counseling programs can also be valuable resources for individuals facing glioblastoma.
In conclusion, the future of glioblastoma treatment is promising, with revolutionary innovations and breakthrough research paving the way for more effective therapies. Immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and novel approaches such as gene therapy and nanotechnology offer new possibilities for treating this aggressive form of brain cancer. Ongoing clinical trials and emerging treatment strategies provide hope for improved outcomes and enhanced survival. Additionally, prioritizing the quality of life for glioblastoma patients through palliative care, integrative therapies, and psychological support is critical in addressing the physical, emotional, and psychological challenges associated with this devastating disease.
FAQ
Question: What is glioblastoma? – Glioblastoma is an aggressive form of brain cancer that originates in the glial cells of the brain. It is characterized by its infiltrative nature and rapid spread within the brain tissue.
Question: What are the current treatment approaches for glioblastoma? – The current treatment options for glioblastoma typically involve surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. These approaches aim to remove as much of the tumor as possible, target any remaining tumor cells, and slow down the growth of new cells.
Question: What are the challenges in glioblastoma treatment? – Glioblastoma treatment faces challenges such as the infiltrative nature of the tumor, drug resistance, heterogeneity of tumor cells, and difficulties in complete surgical removal of the tumor.
Question: How does immunotherapy work in glioblastoma treatment? – Immunotherapy stimulates the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. It can involve immune checkpoint inhibitors that enhance the immune system’s ability to attack the tumor or cancer vaccines that stimulate the immune system to target glioblastoma cells.
Question: What are targeted therapies for glioblastoma? – Targeted therapies are designed to specifically target the genetic alterations or molecular characteristics of cancer cells. Examples include inhibitors that target the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a protein commonly found mutated in glioblastoma.
Question: What are gene therapy and nanotechnology in glioblastoma treatment? – Gene therapy involves introducing genetic material into cells to modify their function. In glioblastoma, gene therapy can deliver therapeutic genes directly to the tumor cells. Nanotechnology utilizes nanoparticles to deliver drugs or therapeutic agents directly to the tumor site, bypassing the blood-brain barrier.
Question: What are some promising clinical trials for glioblastoma treatment? – Ongoing clinical trials explore novel immunotherapies, targeted therapies, and combination treatments for glioblastoma. Combination therapies and localized therapies, such as tumor-treating fields (TTFs), are being investigated.
Question: What are some potential future breakthroughs in glioblastoma treatment? – Future breakthroughs may include new drug delivery systems that can overcome the blood-brain barrier, personalized treatment strategies based on genetic characteristics, and targeting the tumor microenvironment to disrupt the supportive environment for tumor growth.
Question: How can the quality of life for glioblastoma patients be improved? – Palliative care, integrative therapies (acupuncture, massage, yoga), and psychological support (counseling, support groups) play a vital role in addressing the physical, emotional, and psychological challenges faced by glioblastoma patients.