Laser metal cutting technology is revolutionizing the world of metal crafting. Unlike traditional cutting methods, which can be laborious and imprecise, laser cutting offers unmatched precision and versatility. The process involves using a high-powered laser beam to cut through metal sheets with incredible accuracy. This technology finds applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and jewelry design. In this guide, we will delve into the principles, advantages, and types of lasers used in metal cutting. We will also explore the selection and preparation of metals, safety measures, and future trends in this exciting field of laser metal cutting.
Understanding the Principles of Laser Cutting

Source: baisonlaser.com
At the heart of laser metal cutting lies the principle of focused light energy. The beam, generated by stimulating a laser medium, is directed through a series of mirrors and lenses to focus its power on a small spot. When the beam interacts with the alloy surface, it rapidly heats and vaporizes the material, leaving behind a precise cut. The process can be optimized for different thicknesses and intricacy levels. The high level of control and automation in trimming ensures consistent results, making it a preferred choice for intricate and complex designs.
Advantages of Laser Cutting in Metal Crafting
This technology offers a plethora of advantages that set it apart from conventional trimming methods. One of the primary benefits is the exceptional precision it provides. Whether it’s intricate patterns or sharp edges, trimming ensures consistent and accurate results. Additionally, the non-contact nature of trimming reduces the risk of material contamination, making it ideal for industries where cleanliness is paramount. Moreover, the automation and speed of the process significantly reduce production times and costs.
Types of Lasers Used for Cutting
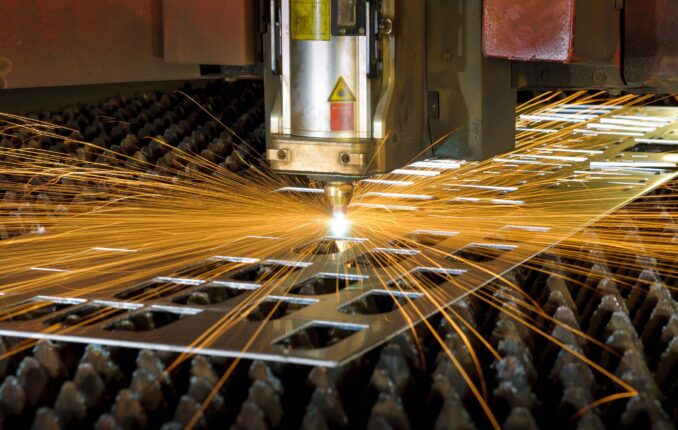

Source: twi-global.com
Several types of lasers are utilized in metal cutting, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The most common ones include CO2, fiber, and neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd: YAG) lasers. CO2 lasers are well-suited for non-metallic materials but can also be cut through thin alloys. Fiber lasers, on the other hand, excel in trimming highly reflective metals like aluminum and copper. Nd: YAG lasers are known for their high power and are typically used for deep welding applications. Choosing the right type depends on the specific requirements of the alloy crafting project.
Selecting the Right Metal
Not all metals are created equal when it comes to cutting. Different metals react differently to the beam due to their varying physical properties. Carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum are among the most commonly used alloys for trimming. Carbon steel is relatively easy to cut, while stainless steel requires higher power due to its reflective nature. Aluminum, on the other hand, demands special considerations to avoid potential thermal distortion.
Preparing Metal Sheets
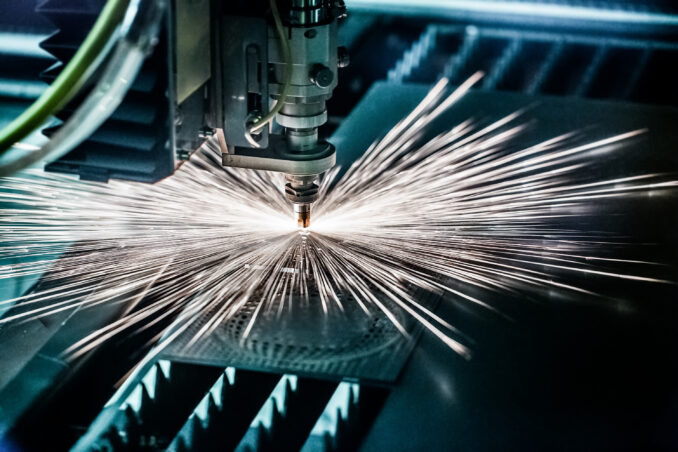
Source: acra.com.au
Before initiating the process, meticulous preparation of the sheets is vital for optimum results. Proper cleaning and removal of any contaminants are essential to avoid imperfections in the final product. The alloy surface should be free of oils, dust, and rust to ensure a smooth and precise cut. Additionally, securing the sheets firmly in place prevents any movement during trimming, minimizing the risk of errors. Effective material handling and positioning are also crucial factors that contribute to the overall success of the process.
Safety Measures
While this is a highly efficient and precise technology, it also comes with inherent safety risks. The powerful beam can cause severe burns or eye injuries if not handled with care. Proper safety equipment, such as safety glasses and protective clothing, should be worn by operators at all times. Enclosed machines help contain the beam and prevent accidental exposure. Adequate ventilation systems should be in place to remove any harmful fumes generated during trimming.
Optimizing Precision
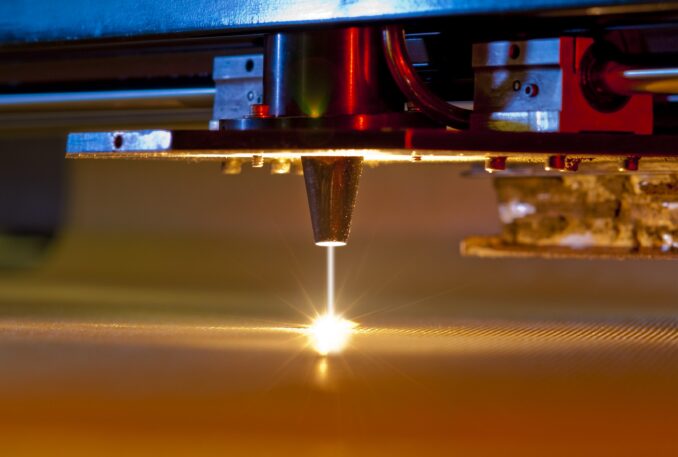

Source: inbound.cammmetals.com
Achieving ultimate precision requires a combination of factors. Fine-tuning laser parameters, such as power, speed, and focus, is crucial to adapt to different thicknesses and types. Regular maintenance of the equipment and optical components ensures consistent performance. Calibration and alignment checks are essential to maintain the accuracy of the trimming process.
Integrating CAD/CAM
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) play a pivotal role in the success of projects. CAD software allows designers to create intricate and detailed designs with ease. These designs can then be converted into machine-readable instructions using CAM software, guiding the trimming machine’s movements. The integration of CAD/CAM streamlines the entire production process, from design to execution, enabling seamless and efficient crafting.
Common Applications of Laser Metal Cutting
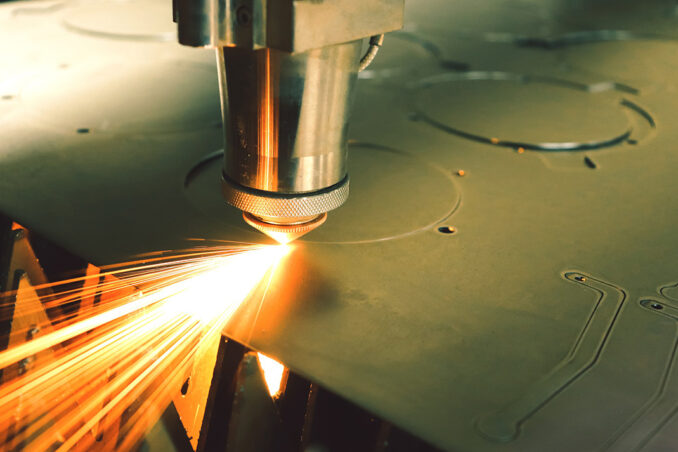

Source: 412metal.com
Laser metal cutting finds applications in various industries and creative pursuits. In the automotive sector, trimming is used to fabricate intricate car body components with tight tolerances. The aerospace industry relies on laser-cut parts for aircraft structures and engine components. In the world of art and jewelry, alloy trimming enables the creation of unique and personalized pieces. Industrial applications include cutting and shaping parts for machinery and equipment.
Future Trends in Laser Metal Cutting Technology
As technology evolves, so does alloy cutting. The future holds exciting prospects for this innovative field. Advancements in sources, such as higher-power fiber lasers, will enable faster speeds and increased thickness capabilities. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) will optimize parameters and enhance automation, reducing the need for manual intervention. Moreover, 3D laser cutting techniques will open up new possibilities for complex and multi-dimensional designs. The continued progress of alloy trimming technology promises to push the boundaries of precision and creativity in crafting.
Conclusion

Source: kaast-usa.com
In conclusion, laser metal cutting technology has emerged as a game-changer in the world of alloy crafting, offering unmatched precision, efficiency, and creative potential. By understanding the principles, types, and material selection, artisans can harness the power of this technology to bring their visions to life. Moreover, strict adherence to safety measures ensures a secure working environment for all involved. As we look ahead, the future of alloy trimming promises even more remarkable advancements, making this cutting-edge technology a cornerstone of modern manufacturing and design. So, embrace the laser and let your metal crafting journey begin!





